Honors
Bio Review Questions Midterm B 2004-05
Modified
True/False
Indicate
whether the sentence or statement is true or false.† If false, change the identified word or
phrase to make the sentence or statement true.
____††††††††† 1.†† Cellular respiration releases energy by
breaking down glucose in the presence of carbon dioxide.
_________________________
____††††††††† 2.†† If an animal cell stops carrying out cellular
respiration, it will die. _________________________
____††††††††† 3.†† The products of glycolysis are 2 ATP,
2 NADH, and 2 pyruvic acid molecules. _________________________
____††††††††† 4.†† Either cellular respiration or fermentation
can be used to release energy, depending on the presence of carbohydrates.
_________________________
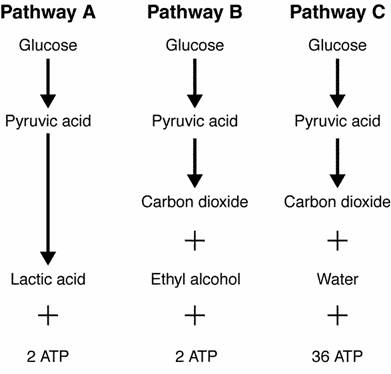
Figure 9-1
____††††††††† 5.†† The pathway labeled A in Figure 9-1 is called
glycolysis. ______________________________
____††††††††† 6.†† If carbon dioxide is present, the
pathway labeled C in Figure 9-1 usually will not occur.
_________________________
____††††††††† 7.†† The Krebs cycle releases energy in the form
of ATP. _________________________
____††††††††† 8.†† Without the Krebs cycle, the electron
transport chain would produce very few ATPs. _________________________
____††††††††† 9.†† ![]() carry electrons from the Krebs cycle to the electron transport chain.
_________________________
carry electrons from the Krebs cycle to the electron transport chain.
_________________________
____††††††††† 10.† In prokaryotes, the electron transport chain
is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
_________________________
____††††††††† 11.† If you swim aerobically for 30 minutes, your
body has probably started to break down stored molecules, such as fats,
for energy. _________________________
____††††††††† 12.† The first few seconds of intense exercise use
up the cellís stores of fat. _________________________
____††††††††† 13.† During the course of a long race, a personís
muscle cells will use both cellular respiration and lactic acid fermentation
to produce ATP. _________________________
____††††††††† 14.† The reactants of photosynthesis are the same
as the reactants of cellular respiration. _________________________
____††††††††† 15.† During photosynthesis, energy is stored in the
form of fats. _________________________
____††††††††† 16.† As a cellís size increases, its ratio of
surface area to volume increases. _________________________
____††††††††† 17.† As a cellís size increases, it places more
demands on its DNA. _________________________
____††††††††† 18.† The smaller a cell is, the more
difficult it is for the cell to move enough materials across its cell membrane.
_________________________
____††††††††† 19.† Cell division solves the problem of cell
growth by increasing cell volume. _________________________
____††††††††† 20.† An imaginary cubic cell with a side length of
10 mm would have a ratio of surface area to volume of 6 : 10.
_________________________
____††††††††† 21.† Most of a cellís growth takes place during the
![]() †phase of the cell cycle.
_________________________
†phase of the cell cycle.
_________________________
____††††††††† 22.† A cellís chromosomes are duplicated during interphase.
_________________________
____††††††††† 23.† If it takes a cell one hour to undergo
mitosis, about 50 minutes of the time would be spent in prophase.
_________________________

Figure 10-2
____††††††††† 24.† The structure shown in Figure 10-2 is a replicated
chromosome. _________________________
____††††††††† 25.† Typically, the longest phase of mitosis is metaphase.
_________________________
____††††††††† 26.† A cell splits into two daughter cells during telophase.
_________________________
____††††††††† 27.† Normal cells stop growing when they
come into contact with other cells. _________________________
____††††††††† 28.† Proteins called cyclins help regulate
the cell cycle. _________________________
____††††††††† 29.† Cancer is a disorder in which some of
the bodyís cells lose the ability to control growth and division.
_________________________
____††††††††† 30.† Lack of control over mitosis is the
cause of all cancers. ______________________________
____††††††††† 31.† A trait is a specific characteristic that varies
from one individual to another. _________________________
____††††††††† 32.† Gregor Mendel concluded that the tall plants
in the P generation passed the factor for tallness to the F1
generation. _________________________
____††††††††† 33.† An organism with a dominant allele for a
particular form of a trait will sometimes show that trait. _________________________
____††††††††† 34.† True-breeding plants that produced axial
flowers were crossed with true-breeding plants that produced terminal flowers.
The resulting offspring produced terminal flowers because the allele for
terminal flowers is recessive. _________________________
____††††††††† 35.† When alleles segregate from each other, they join.
_________________________
____††††††††† 36.† If the alleles for a trait did not segregate
during gamete formation, offspring would always show the trait of at
least one of the parents. _________________________
____††††††††† 37.† The principles of probability can explain
the numerical results of Mendelís experiments. _________________________
____††††††††† 38.† The probability that a gamete produced by a
pea plant heterozygous for stem height (Tt) will contain the recessive
allele is 100%. _________________________
____††††††††† 39.† If roan cows and roan bulls are mated,
according to the principle of codominance, 25% of the offspring are
expected to be roan. _________________________
____††††††††† 40.† Coat color in rabbits is determined by a
single gene that has multiple alleles. _________________________
____††††††††† 41.† If an organism has 16 chromosomes in each of
its egg cells, the organismís diploid number is 32.
_________________________
____††††††††† 42.† If an organism is heterozygous for a
particular gene, the two different alleles will be separated during anaphase
II of meiosis, assuming that no crossing-over has occurred.
_________________________
____††††††††† 43.† Mitosis results in two cells, whereas meiosis
results in one cell. _________________________
____††††††††† 44.† If an organism has four linkage groups, it has
eight chromosomes. _________________________
____††††††††† 45.† Genes in the same linkage group are usually
inherited separately. _________________________
____††††††††† 46.† In eukaryotes, DNA replication proceeds in one
direction down the DNA molecule. _________________________
____††††††††† 47.† The replication of a DNA molecule results in four
copies of the same gene. _________________________
____††††††††† 48.† DNA is tightly wrapped around nucleosomes.
_________________________
____††††††††† 49.† If a nucleic acid contains uracil, it is DNA.
_________________________
____††††††††† 50.† The nitrogenous bases in RNA are able
to form hydrogen bonds with each other. _________________________
____††††††††† 51.† During DNA replication, only one strand
of DNA serves as a template. _________________________
____††††††††† 52.† A codon consists of four nucleotides.
_________________________
____††††††††† 53.† The anticodon AGA is complementary to the
codon TCT. _________________________
____††††††††† 54.† Genes determine a personís eye color by coding
for nitrogenous bases that affect eye color. _________________________
____††††††††† 55.† DNA codes for DNA polymerase.
_________________________
____††††††††† 56.† Without regulatory sites, the
expression of a gene would not be controlled. _________________________
____††††††††† 57.† In prokaryotes, an operon is a group of
genes that are operated together. _________________________
____††††††††† 58.† Gene regulation in eukaryotes is less
complex than in prokaryotes. _________________________
____††††††††† 59.† The TATA box in eukaryotes helps to
ensure transcription. _________________________
____††††††††† 60.† In fruit flies, the hox gene that controls the
development of the wings is located before the hox gene that controls
the development of the eye and before the hox gene that controls the
development of the tail. _________________________
Multiple
Choice
Identify
the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
question.
____††††††††† 61.† Which of the following is NOT a stage of
cellular respiration?
|
a. |
fermentation |
|
b. |
electron transport |
|
c. |
glycolysis |
|
d. |
Krebs cycle |
____††††††††† 62.† Which of the following is the correct sequence
of events in cellular respiration?
|
a. |
glycolysis ģ fermentation
ģ Krebs
cycle |
|
b. |
Krebs cycle ģ electron
transport ģ
glycolysis |
|
c. |
glycolysis ģ Krebs cycle ģ electron
transport |
|
d. |
Krebs cycle ģ glycolysis ģ electron
transport |
____††††††††† 63.† Which of the following is released during
cellular respiration?
|
a. |
oxygen |
|
b. |
air |
|
c. |
energy |
|
d. |
lactic acid |
____††††††††† 64.† Cellular respiration uses one molecule of
glucose to produce
|
a. |
2 ATP molecules. |
|
b. |
34 ATP molecules. |
|
c. |
36 ATP molecules. |
|
d. |
38 ATP molecules. |
____††††††††† 65.† What is the correct equation for cellular
respiration?
|
a. |
6O2 + C6H12O6
ģ 6CO2
+ 6H2O + Energy |
|
b. |
6O2 + C6H12O6
+ Energy ģ 6CO2
+ 6H2O |
|
c. |
6CO2 + 6H2O ģ 6O2
+ C6H12O6 + Energy |
|
d. |
6CO2 + 6H2O +
Energy ģ 6O2
+ C6H12O6 |
____††††††††† 66.† Cellular respiration releases energy by
breaking down
|
a. |
food molecules. |
|
b. |
ATP. |
|
c. |
carbon dioxide. |
|
d. |
water. |
____††††††††† 67.† What are the reactants in the equation for
cellular respiration?
|
a. |
oxygen and lactic acid |
|
b. |
carbon dioxide and water |
|
c. |
glucose and oxygen |
|
d. |
water and glucose |
____††††††††† 68.† Which of these is a product of cellular
respiration?
|
a. |
oxygen |
|
b. |
water |
|
c. |
glucose |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 69.† Which of these processes takes place in the
cytoplasm of a cell?
|
a. |
glycolysis |
|
b. |
electron transport |
|
c. |
Krebs cycle |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 70.† Glycolysis provides a cell with a net gain of
|
a. |
2 ATP molecules. |
|
b. |
4 ATP molecules. |
|
c. |
18 ATP molecules. |
|
d. |
36 ATP molecules. |
____††††††††† 71.† The starting molecule for glycolysis is
|
a. |
ADP. |
|
b. |
pyruvic acid. |
|
c. |
citric acid. |
|
d. |
glucose. |
____††††††††† 72.† Glycolysis requires
|
a. |
an energy input. |
|
b. |
oxygen. |
|
c. |
hours to produce many ATP molecules. |
|
d. |
NADP+. |
____††††††††† 73.† Which of the following is NOT a product of
glycolysis?
|
a. |
NADH |
|
b. |
pyruvic acid |
|
c. |
ATP |
|
d. |
glucose |
____††††††††† 74.† Which of the following acts as an electron
carrier in cellular respiration?
|
a. |
NAD+ |
|
b. |
pyruvic acid |
|
c. |
ADP |
|
d. |
ATP |
____††††††††† 75.† Lactic acid fermentation occurs in
|
a. |
bread dough. |
|
b. |
any environment containing oxygen. |
|
c. |
muscle cells. |
|
d. |
mitochondria. |
____††††††††† 76.† The two main types of fermentation are called
|
a. |
alcoholic and aerobic. |
|
b. |
aerobic and anaerobic. |
|
c. |
alcoholic and lactic acid. |
|
d. |
lactic acid and anaerobic. |
____††††††††† 77.† One cause of muscle soreness is
|
a. |
alcoholic fermentation. |
|
b. |
glycolysis. |
|
c. |
lactic acid fermentation. |
|
d. |
the Krebs cycle. |
____††††††††† 78.† Which process is used to produce beer and
wine?
|
a. |
lactic acid fermentation |
|
b. |
glycolysis |
|
c. |
alcoholic fermentation |
|
d. |
the Krebs cycle |
____††††††††† 79.† Milk is converted to yogurt under certain
conditions when the microorganisms in the milk produce acid. Which of these
processes would you expect to be key in the production of yogurt?
|
a. |
the Krebs cycle |
|
b. |
photosynthesis |
|
c. |
alcoholic fermentation |
|
d. |
lactic acid fermentation |
____††††††††† 80.† During lactic acid fermentation,
|
a. |
NAD+ is regenerated, allowing
glycolysis to continue. |
|
b. |
glucose is split into three pyruvic acid
molecules. |
|
c. |
oxygen is required. |
|
d. |
3 ATP molecules are produced. |
____††††††††† 81.† The conversion of pyruvic acid into lactic
acid requires
|
a. |
alcohol. |
|
b. |
oxygen. |
|
c. |
ATP. |
|
d. |
NADH. |
____††††††††† 82.† In the presence of oxygen, glycolysis is
followed by
|
a. |
lactic acid fermentation. |
|
b. |
alcoholic fermentation. |
|
c. |
photosynthesis. |
|
d. |
the Krebs cycle. |
____††††††††† 83.† Cellular respiration is called an aerobic
process because it requires
|
a. |
light. |
|
b. |
exercise. |
|
c. |
oxygen. |
|
d. |
glucose. |
____††††††††† 84.† Which organism is NOT likely to carry out
cellular respiration?
|
a. |
tree |
|
b. |
mushroom |
|
c. |
anaerobic bacterium |
|
d. |
tiger |
____††††††††† 85.† The starting molecule for the Krebs cycle is
|
a. |
glucose. |
|
b. |
NADH. |
|
c. |
pyruvic acid. |
|
d. |
coenzyme A. |
____††††††††† 86.† The Krebs cycle does not occur if
|
a. |
oxygen is present. |
|
b. |
fermentation occurs. |
|
c. |
glycolysis occurs. |
|
d. |
carbon dioxide is present. |
____††††††††† 87.† During one turn, the Krebs cycle produces
|
a. |
oxygen. |
|
b. |
lactic acid. |
|
c. |
electron carriers. |
|
d. |
glucose. |
____††††††††† 88.† The Krebs cycle starts with
|
a. |
lactic acid and yields carbon dioxide. |
|
b. |
glucose and yields 32 ATPs. |
|
c. |
pyruvic acid and yields lactic acid or
alcohol. |
|
d. |
pyruvic acid and yields carbon dioxide. |
____††††††††† 89.† The electron transport chain can be found in
|
a. |
prokaryotes. |
|
b. |
animals. |
|
c. |
plants. |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 90.† In eukaryotes, electron transport occurs in
the
|
a. |
mitochondria. |
|
b. |
chloroplasts. |
|
c. |
cell membrane. |
|
d. |
cytoplasm. |
____††††††††† 91.† Which of the following passes high-energy
electrons into the electron transport chain?
|
a. |
NADH and FADH2 |
|
b. |
ATP and ADP |
|
c. |
citric acid |
|
d. |
acetyl Ė CoA |
____††††††††† 92.† Each pair of high-energy electrons that moves
down the electron transport chain provides enough energy to
|
a. |
transport water molecules across the
membrane. |
|
b. |
convert 3 ADP molecules into 3 ATP
molecules. |
|
c. |
convert carbon dioxide into water
molecules. |
|
d. |
break glucose into pyruvic acid. |
____††††††††† 93.† The energy of the electrons passing along the
electron transport chain is used to make
|
a. |
lactic acid. |
|
b. |
citric acid. |
|
c. |
alcohol. |
|
d. |
ATP. |
____††††††††† 94.† Breathing heavily after running a race is your
bodyís way of
|
a. |
making more citric acid. |
|
b. |
repaying an oxygen debt. |
|
c. |
restarting glycolysis. |
|
d. |
recharging the electron transport chain. |
____††††††††† 95.† When the body needs to exercise for longer
than 90 seconds, it generates ATP by carrying out
|
a. |
lactic acid fermentation. |
|
b. |
alcoholic fermentation. |
|
c. |
cellular respiration. |
|
d. |
glycolysis. |
____††††††††† 96.† If you want to control your weight, how long
should you exercise aerobically each time that you exercise?
|
a. |
at least 90 seconds |
|
b. |
less than 15 minutes |
|
c. |
15 to 20 minutes |
|
d. |
more than 20 minutes |
____††††††††† 97.† The energy needed to win a 2-minute footrace
is produced mostly by
|
a. |
lactic acid fermentation. |
|
b. |
cellular respiration. |
|
c. |
using up stores of ATP. |
|
d. |
breaking down fats. |
____††††††††† 98.† Which statement mainly explains why even
well-conditioned athletes have to pace themselves for athletic events that last
several hours?
|
a. |
Lactic acid fermentation can cause
muscle soreness. |
|
b. |
Heavy breathing is needed to get rid of
lactic acid. |
|
c. |
Cellular respiration releases energy
more slowly than fermentation does. |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 99.† All of the following are sources of energy
during exercise EXCEPT
|
a. |
stored ATP. |
|
b. |
alcoholic fermentation. |
|
c. |
lactic acid fermentation. |
|
d. |
cellular respiration. |
____††††††††† 100.††††††††††† Which process does NOT release
energy from glucose?
|
a. |
glycolysis |
|
b. |
photosynthesis |
|
c. |
fermentation |
|
d. |
cellular respiration |
____††††††††† 101.††††††††††† How are cellular respiration and
photosynthesis almost opposite processes?
|
a. |
Photosynthesis releases energy, and
cellular respiration stores energy. |
|
b. |
Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide
from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back. |
|
c. |
Photosynthesis removes oxygen from the
atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back. |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 102.††††††††††† Photosynthesis is to chloroplasts as
cellular respiration is to
|
a. |
chloroplasts. |
|
b. |
cytoplasm. |
|
c. |
mitochondria. |
|
d. |
nuclei. |
____††††††††† 103.††††††††††† Unlike photosynthesis, cellular
respiration occurs in
|
a. |
animal cells only. |
|
b. |
plant cells only. |
|
c. |
all but plant cells. |
|
d. |
all eukaryotic cells. |
____††††††††† 104.††††††††††† Plants cannot release energy from
glucose using
|
a. |
glycolysis. |
|
b. |
photosynthesis. |
|
c. |
the Krebs cycle. |
|
d. |
cellular respiration. |
____††††††††† 105.††††††††††† The products of photosynthesis are
the
|
a. |
products of cellular respiration. |
|
b. |
reactants of cellular respiration. |
|
c. |
products of glycolysis. |
|
d. |
reactants of fermentation. |
____††††††††† 106.††††††††††† As a cell becomes larger, its
|
a. |
volume increases faster than its surface
area. |
|
b. |
surface area increases faster than its
volume. |
|
c. |
volume increases, but its surface area
stays the same. |
|
d. |
surface area stays the same, but its
volume increases. |
____††††††††† 107.††††††††††† As a cell grows, it
|
a. |
places more demands on its DNA. |
|
b. |
uses up food and oxygen more quickly. |
|
c. |
has more trouble moving enough materials
across its cell membrane. |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 108.††††††††††† If the length of a cell increases 10
times, its volume increases about
|
a. |
5 times. |
|
b. |
10 times. |
|
c. |
100 times. |
|
d. |
1000 times. |
____††††††††† 109.††††††††††† The speed with which wastes are
produced by a cell depends on the cellís
|
a. |
ratio of surface area to volume. |
|
b. |
environment. |
|
c. |
volume. |
|
d. |
surface area. |
____††††††††† 110.††††††††††† All of the following are problems
that growth causes for cells EXCEPT
|
a. |
DNA overload. |
|
b. |
excess oxygen. |
|
c. |
obtaining enough food. |
|
d. |
expelling wastes. |
____††††††††† 111.††††††††††† Compared to small cells, large cells
have more trouble
|
a. |
dividing. |
|
b. |
producing daughter cells. |
|
c. |
moving needed materials in and waste
products out. |
|
d. |
making copies of their DNA. |
____††††††††† 112.††††††††††† The process by which a cell divides
into two daughter cells is called
|
a. |
cell division. |
|
b. |
metaphase. |
|
c. |
interphase. |
|
d. |
mitosis. |
____††††††††† 113.††††††††††† Which of the following is NOT a way
that cell division solves the problems of cell growth?
|
a. |
Cell division provides each daughter
cell with its own copy of DNA. |
|
b. |
Cell division increases the mass of the
original cell. |
|
c. |
Cell division increases the surface area
of the original cell. |
|
d. |
Cell division reduces the original
cellís volume. |
____††††††††† 114.††††††††††† If a normal cell divides, you can
assume that
|
a. |
its surface area has become larger than
its volume. |
|
b. |
its volume has become larger than its
surface area. |
|
c. |
it has grown to its full size. |
|
d. |
it has grown too large to meet its
needs. |
____††††††††† 115.††††††††††† If a cellís DNA were not copied
before cell division, the cell could
|
a. |
have a DNA overload. |
|
b. |
become cancerous. |
|
c. |
fail to exchange materials. |
|
d. |
divide. |
____††††††††† 116.††††††††††† Which of the following happens when
a cell divides?
|
a. |
The cellís volume increases. |
|
b. |
It becomes more difficult for the cell
to get enough oxygen and nutrients. |
|
c. |
The cell has DNA overload. |
|
d. |
Each daughter cell receives its own copy
of the parent cellís DNA. |
____††††††††† 117.††††††††††† When during the cell cycle are
chromosomes visible?
|
a. |
only during interphase |
|
b. |
only when they are being replicated |
|
c. |
only during cell division |
|
d. |
only during the G1 phase |
____††††††††† 118.††††††††††† Which of the following is a phase in
the cell cycle?
|
a. |
G1 phase |
|
b. |
G2 phase |
|
c. |
M phase |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 119.††††††††††† Which pair is correct?
|
a. |
G1 phase, DNA replication |
|
b. |
G2 phase, preparation for
mitosis |
|
c. |
S phase, cell division |
|
d. |
M phase, cell growth |
____††††††††† 120.††††††††††† When during the cell cycle is a
cellís DNA replicated?
|
a. |
G1 phase |
|
b. |
G2 phase |
|
c. |
S phase |
|
d. |
M phase |
____††††††††† 121.††††††††††† Which event occurs during
interphase?
|
a. |
The cell grows. |
|
b. |
Centrioles appear. |
|
c. |
Spindle fibers begin to form. |
|
d. |
Centromeres divide. |
____††††††††† 122.††††††††††† Which of the following is a correct
statement about the events of the cell cycle?
|
a. |
Little happens during the G1
and G2 phases. |
|
b. |
DNA replicates during cytokinesis. |
|
c. |
The M phase is usually the longest
phase. |
|
d. |
Interphase consists of the G1,
S, and, G2 phases. |
____††††††††† 123.††††††††††† Which of the following is NOT a
correct statement about the events of the cell cycle?
|
a. |
Interphase is usually the longest phase. |
|
b. |
DNA replicates during the S phase. |
|
c. |
Cell division ends with cytokinesis. |
|
d. |
The cell grows during the G2
phase. |
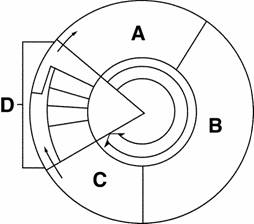
Figure 10-1
____††††††††† 124.††††††††††† Cell division is represented in
Figure 10-1 by the letter
|
a. |
A. |
|
b. |
B. |
|
c. |
C. |
|
d. |
D. |
____††††††††† 125.††††††††††† The cell cycle is the
|
a. |
series of events that cells go through
as they grow and divide. |
|
b. |
period of time between the birth and the
death of a cell. |
|
c. |
time from prophase until cytokinesis. |
|
d. |
time it takes for one cell to undergo
mitosis. |

Figure 10-2
____††††††††† 126.††††††††††† The structure labeled A in Figure
10-2 is called the
|
a. |
centromere. |
|
b. |
centriole. |
|
c. |
sister chromatid. |
|
d. |
spindle. |
____††††††††† 127.††††††††††† The structures labeled B in Figure
10-2 are called
|
a. |
centromeres. |
|
b. |
centrioles. |
|
c. |
sister chromatids. |
|
d. |
spindles. |
____††††††††† 128.††††††††††† During which phase(s) of mitosis are
structures like the one shown in Figure 10-2 visible?
|
a. |
anaphase and prophase |
|
b. |
prophase and metaphase |
|
c. |
metaphase only |
|
d. |
anaphase and interphase |
____††††††††† 129.††††††††††† Which of the following is a phase of
mitosis?
|
a. |
cytokinesis |
|
b. |
interphase |
|
c. |
prophase |
|
d. |
S phase |
____††††††††† 130.††††††††††† The first phase of mitosis is called
|
a. |
prophase. |
|
b. |
anaphase. |
|
c. |
metaphase. |
|
d. |
interphase. |
____††††††††† 131.††††††††††† During which phase of mitosis do the
chromosomes line up along the middle of the dividing cell?
|
a. |
prophase |
|
b. |
telophase |
|
c. |
metaphase |
|
d. |
anaphase |
____††††††††† 132.††††††††††† Which of the following represents
the phases of mitosis in their proper sequence?
|
a. |
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
|
b. |
interphase, prophase, metaphase,
anaphase, telophase |
|
c. |
interphase, prophase, metaphase,
telophase |
|
d. |
prophase, metaphase, anaphase,
telophase, cytokinesis |
____††††††††† 133.††††††††††† What is the role of the spindle
during mitosis?
|
a. |
It helps separate the chromosomes. |
|
b. |
It breaks down the nuclear membrane. |
|
c. |
It duplicates the DNA. |
|
d. |
It divides the cell in half. |
____††††††††† 134.††††††††††† The two main stages of cell division
are called
|
a. |
mitosis and interphase. |
|
b. |
synthesis and cytokinesis. |
|
c. |
the M phase and the S phase. |
|
d. |
cytokinesis and mitosis. |
____††††††††† 135.††††††††††† One difference between cell division
in plant cells and in animal cells is that plant cells have
|
a. |
centrioles. |
|
b. |
centromeres. |
|
c. |
a cell plate. |
|
d. |
chromatin. |
____††††††††† 136.††††††††††† During normal mitotic cell division,
a parent cell having four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each
containing
|
a. |
two chromosomes. |
|
b. |
four chromosomes. |
|
c. |
eight chromosomes. |
|
d. |
sixteen chromosomes. |
____††††††††† 137.††††††††††† What happens when cells come into
contact with other cells?
|
a. |
They divide more quickly. |
|
b. |
They stop growing. |
|
c. |
They produce cyclins. |
|
d. |
They produce p53. |
____††††††††† 138.††††††††††† Which of the following is a factor
that can stop normal cells from growing?
|
a. |
contact with other cells |
|
b. |
growth factors |
|
c. |
a cut in the skin |
|
d. |
cyclin that has been taken from a cell
in mitosis |
____††††††††† 139.††††††††††† Cells grown in a petri dish tend to
divide until they form a thin layer covering the bottom of the dish. If cells
are removed from the middle of the dish, the cells bordering the open space
will begin dividing until they have filled the empty space. What does this
experiment show?
|
a. |
When cells come into contact with other
cells, they stop growing. |
|
b. |
The controls on cell growth and division
can be turned on and off. |
|
c. |
Cell division can be regulated by
factors outside the cell. |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 140.††††††††††† Which of the following explains why
normal cells grown in a petri dish tend to stop growing once they have covered
the bottom of the dish?
|
a. |
The cells lack cyclin. |
|
b. |
The petri dish inhibits cell growth. |
|
c. |
Contact with other cells stops cell
growth. |
|
d. |
Most cells grown in petri dishes have a
defective p53. |
____††††††††† 141.††††††††††† When cytoplasm from a cell that is
undergoing mitosis is injected into a cell that is in interphase, the second
cell
|
a. |
stays in interphase. |
|
b. |
enters mitosis. |
|
c. |
stops making cyclin. |
|
d. |
loses its p53. |
____††††††††† 142.††††††††††† In eukaryotic cells, the timing of
the cell cycle is regulated by
|
a. |
the centrioles. |
|
b. |
cyclins. |
|
c. |
the spindle. |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 143.††††††††††† Cyclins are a family of closely
related proteins that
|
a. |
regulate the cell cycle. |
|
b. |
produce p53. |
|
c. |
cause cancer. |
|
d. |
work to heal wounds. |
____††††††††† 144.††††††††††† Which of the following regulate(s)
the cell cycle?
|
a. |
growth factors |
|
b. |
cyclins |
|
c. |
p53 |
|
d. |
all of the above |
____††††††††† 145.††††††††††† Which of the following is an
internal regulator of the cell cycle?
|
a. |
cyclins |
|
b. |
growth factors |
|
c. |
the mitotic spindle |
|
d. |
cancer cells |
____††††††††† 146.††††††††††† Cancer is a disorder in which some
cells have lost the ability to control their
|
a. |
size. |
|
b. |
spindle fibers. |
|
c. |
growth rate. |
|
d. |
surface area. |
____††††††††† 147.††††††††††† Cancer cells form masses of cells
called
|
a. |
tumors. |
|
b. |
cyclins. |
|
c. |
growth factors. |
|
d. |
p53. |
____††††††††† 148.††††††††††† A cell with a defective p53 gene is
likely to
|
a. |
divide regularly. |
|
b. |
stop dividing. |
|
c. |
accumulate chromosomal damage. |
|
d. |
combat tumors. |
____††††††††† 149.††††††††††† Cancer affects
|
a. |
humans only. |
|
b. |
most unicellular organisms. |
|
c. |
multicellular organisms. |
|
d. |
unicellular organisms. |
____††††††††† 150.††††††††††† What is a tumor?
|
a. |
an accumulation of cyclins |
|
b. |
a mass of cancer cells |
|
c. |
the rapidly dividing cells found at the
site of a wound |
|
d. |
a defective p53 gene |
____††††††††† 151.††††††††††† Gregor Mendel used pea plants to
study
|
a. |
flowering. |
|
b. |
gamete formation. |
|
c. |
the inheritance of traits. |
|
d. |
cross-pollination. |
____††††††††† 152.††††††††††† Offspring that result from crosses
between true-breeding parents with different traits
|
a. |
are true-breeding. |
|
b. |
make up the F2 generation. |
|
c. |
make up the parental generation. |
|
d. |
are called hybrids. |
____††††††††† 153.††††††††††† Gregor Mendel removed the male parts
from the flowers of some plants in order to
|
a. |
prevent hybrids from forming. |
|
b. |
prevent cross-pollination. |
|
c. |
prevent self-pollination. |
|
d. |
make controlled crosses between plants. |
____††††††††† 154.††††††††††† The chemical factors that determine
traits are called
|
a. |
alleles. |
|
b. |
traits. |
|
c. |
genes. |
|
d. |
characters. |
____††††††††† 155.††††††††††† Gregor Mendel concluded that traits
are
|
a. |
not inherited by offspring. |
|
b. |
inherited through the passing of factors
from parents to offspring. |
|
c. |
determined by dominant factors only. |
|
d. |
determined by recessive factors only. |
____††††††††† 156.††††††††††† When Gregor Mendel crossed a tall
plant with a short plant, the F1 plants inherited
|
a. |
an allele for tallness from each parent. |
|
b. |
an allele for tallness from the tall
parent and an allele for shortness from the short parent. |
|
c. |
an allele for shortness from each
parent. |
|
d. |
an allele from only the tall parent. |
____††††††††† 157.††††††††††† The principle of dominance states
that
|
a. |
all alleles are dominant. |
|
b. |
all alleles are recessive. |
|
c. |
some alleles are dominant and others are
recessive. |
|
d. |
alleles are neither dominant nor
recessive. |
____††††††††† 158.††††††††††† When Gregor Mendel crossed
true-breeding tall plants with true-breeding short plants, all the offspring
were tall because
|
a. |
the allele for tall plants is recessive. |
|
b. |
the allele for short plants is dominant. |
|
c. |
the allele for tall plants is dominant. |
|
d. |
they were true-breeding like their
parents. |
____††††††††† 159.††††††††††† If a pea plant has a recessive
allele for green peas, it will produce
|
a. |
green peas if it also has a dominant
allele for yellow peas. |
|
b. |
both green peas and yellow peas if it
also has a dominant allele for yellow peas. |
|
c. |
green peas if it does not also have a
dominant allele for yellow peas. |
|
d. |
yellow peas if it does not also have a
dominant allele for green peas. |
____††††††††† 160.††††††††††† A tall plant is crossed with a short
plant. If the tall F1 pea plants are allowed to self-pollinate,
|
a. |
the offspring will be of medium height. |
|
b. |
all of the offspring will be tall. |
|
c. |
all of the offspring will be short. |
|
d. |
some of the offspring will be tall, and
some will be short. |
____††††††††† 161.††††††††††† In the P generation, a tall plant
was crossed with a short plant. Short plants reappeared in the F2
generation because
|
a. |
some of the F2 plants
produced gametes that carried the allele for shortness. |
|
b. |
the allele for shortness is dominant. |
|
c. |
the allele for shortness and the allele
for tallness segregated when the F1 plants produced gametes. |
|
d. |
they inherited an allele for shortness
from one parent and an allele for tallness from the other parent. |
____††††††††† 162.††††††††††† In the P generation, a tall plant
was crossed with a short plant. If alleles did not segregate during gamete
formation,
|
a. |
all of the F1 plants would be
short. |
|
b. |
some of the F1 plants would
be tall and some would be short. |
|
c. |
all of the F2 would be short. |
|
d. |
all of the F2 plants would be
tall. |
____††††††††† 163.††††††††††† When you flip a coin, what is the
probability that it will come up tails?
|
a. |
1/2 |
|
b. |
1/4 |
|
c. |
1/8 |
|
d. |
1 |
____††††††††† 164.††††††††††† The principles of probability can be
used to
|
a. |
predict the traits of the offspring
produced by genetic crosses. |
|
b. |
determine the actual outcomes of genetic
crosses. |
|
c. |
predict the traits of the parents used
in genetic crosses. |
|
d. |
decide which organisms are best to use
in genetic crosses. |
____††††††††† 165.††††††††††† In the P generation, a tall plant is
crossed with a short plant. The probability that an F2 plant will be
tall is
|
a. |
50%. |
|
b. |
75%. |
|
c. |
25%. |
|
d. |
100%. |
____††††††††† 166.††††††††††† Organisms that have two identical
alleles for a particular trait are said to be
|
a. |
hybrid. |
|
b. |
homozygous. |
|
c. |
heterozygous. |
|
d. |
dominant. |
|
|
|
Tt |
||
|
|
|
T |
t |
|
|
TT |
T |
TT |
Tt |
|
|
T |
TT |
Tt |
||
|
T |
= |
tall |
|
t |
= |
short |
Figure 11-1
____††††††††† 167.††††††††††† In the Punnett square shown in
Figure 11-1, which of the following is true about the offspring resulting from
the cross?
|
a. |
About half are expected to be short. |
|
b. |
All are expected to be short. |
|
c. |
About half are expected to be tall. |
|
d. |
All are expected to be tall. |
____††††††††† 168.††††††††††† A Punnett square shows all of the
following EXCEPT
|
a. |
all possible results of a genetic cross. |
|
b. |
the genotypes of the offspring. |
|
c. |
the alleles in the gametes of each
parent. |
|
d. |
the actual results of a genetic cross. |
____††††††††† 169.††††††††††† If you made a Punnett square showing
Gregor Mendelís cross between true-breeding tall plants and true-breeding short
plants, the square would show that the offspring had
|
a. |
the genotype of one of the parents. |
|
b. |
a phenotype that was different from that
of both parents. |
|
c. |
a genotype that was different from that
of both parents. |
|
d. |
the genotype of both parents. |
____††††††††† 170.††††††††††† What principle states that during
gamete formation genes for different traits separate without influencing each
otherís inheritance?
|
a. |
principle of dominance |
|
b. |
principle of independent assortment |
|
c. |
principle of probabilities |
|
d. |
principle of segregation |
|
RrYy |
||||||
|
|
|
RY |
Ry |
rY |
ry |
|
|
|
RY |
RRYY |
RRYy |
RrYY |
RrYy |
Seed Shape R Ė round r Ė wrinkled |
|
RrYy |
Ry |
RRYy |
RRyy |
RrYy |
Rryy |
Seed Color Y Ė yellow y Ė green |
|
rY |
RrYY |
RrYy |
rrYY |
rrYy |
||
|
|
ry |
RrYy |
Rryy |
rrYy |
rryy |
|
Figure 11-2
____††††††††† 171.††††††††††† The Punnett square in Figure 11-2
shows that the gene for pea shape and the gene for pea color
|
a. |
assort independently. |
|
b. |
are linked. |
|
c. |
have the same alleles. |
|
d. |
are always homozygous. |
____††††††††† 172.††††††††††† How many different allele
combinations would be found in the gametes produced by a pea plant whose
genotype was RrYY?
|
a. |
2 |
|
b. |
4 |
|
c. |
8 |
|
d. |
16 |
____††††††††† 173.††††††††††† If a pea plant that is heterozygous
for round, yellow peas (RrYy) is crossed with a pea plant that is
homozygous for round peas but heterozygous for yellow peas (RRYy), how
many different phenotypes are their offspring expected to show?
|
a. |
2 |
|
b. |
4 |
|
c. |
8 |
|
d. |
16 |
____††††††††† 174.††††††††††† Situations in which one allele for a
gene is not completely dominant over another allele for that gene are called
|
a. |
multiple alleles. |
|
b. |
incomplete dominance. |
|
c. |
polygenic inheritance. |
|
d. |
multiple genes. |
____††††††††† 175.††††††††††† A cross of a red cow (RR) with a
white bull (WW) produces all roan offspring (RRWW). This type of inheritance is
known as
|
a. |
incomplete dominance. |
|
b. |
polygenic inheritance. |
|
c. |
codominance. |
|
d. |
multiple alleles. |
____††††††††† 176.††††††††††† Variation in human skin color is a
result of
|
a. |
incomplete dominance. |
|
b. |
codominance. |
|
c. |
polygenic traits. |
|
d. |
multiple alleles. |
____††††††††† 177.††††††††††† Gregor Mendelís principles of
genetics apply to
|
a. |
plants only. |
|
b. |
animals only. |
|
c. |
pea plants only. |
|
d. |
all organisms. |
____††††††††† 178.††††††††††† Why did Thomas Hunt Morgan use fruit
flies in his studies?
|
a. |
Fruit flies produce a large number of
offspring. |
|
b. |
Fruit flies take a long time to produce
offspring. |
|
c. |
Fruit flies share certain
characteristics with pea plants. |
|
d. |
Fruit flies have a long lifespan. |
____††††††††† 179.††††††††††† A man and a woman who are both
heterozygous for normal skin pigmentation (Aa) produce an albino
offspring (aa). Which of Mendelís principles explain(s) why the
offspring is albino?
|
a. |
dominance only |
|
b. |
independent assortment only |
|
c. |
dominance and segregation |
|
d. |
segregation only |
____††††††††† 180.††††††††††† The number of chromosomes in a
gamete is represented by the symbol
|
a. |
Z. |
|
b. |
X. |
|
c. |
N. |
|
d. |
Y. |
____††††††††† 181.††††††††††† If an organismís diploid number is
12, its haploid number is
|
a. |
12. |
|
b. |
6. |
|
c. |
24. |
|
d. |
3. |
____††††††††† 182.††††††††††† Gametes have
|
a. |
homologous chromosomes. |
|
b. |
twice the number of chromosomes found in
body cells. |
|
c. |
two sets of chromosomes. |
|
d. |
one allele for each gene. |
____††††††††† 183.††††††††††† Gametes are produced by the process
of
|
a. |
mitosis. |
|
b. |
meiosis. |
|
c. |
crossing-over. |
|
d. |
replication. |
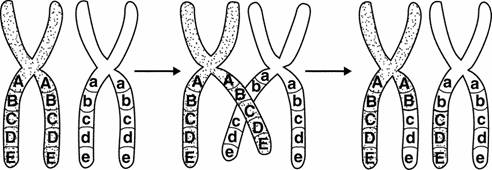
Figure 11-3
____††††††††† 184.††††††††††† What is shown in Figure 11-3?
|
a. |
independent assortment |
|
b. |
anaphase I of meiosis |
|
c. |
crossing-over |
|
d. |
replication |
____††††††††† 185.††††††††††† Chromosomes form tetrads during
|
a. |
prophase of meiosis I. |
|
b. |
metaphase of meiosis I. |
|
c. |
interphase. |
|
d. |
anaphase of meiosis II. |
____††††††††† 186.††††††††††† What happens between meiosis I and
meiosis II that reduces the number of chromosomes?
|
a. |
Crossing-over occurs. |
|
b. |
Metaphase occurs. |
|
c. |
Replication occurs twice. |
|
d. |
Replication does not occur. |
____††††††††† 187.††††††††††† Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in
the formation of
|
a. |
diploid cells. |
|
b. |
haploid cells. |
|
c. |
2N daughter cells. |
|
d. |
body cells. |
____††††††††† 188.††††††††††† Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in
the formation of
|
a. |
two genetically identical cells. |
|
b. |
four genetically different cells. |
|
c. |
four genetically identical cells. |
|
d. |
two genetically different cells. |
____††††††††† 189.††††††††††† Crossing-over rarely occurs in
mitosis, unlike meiosis. Which of the following is the likely reason?
|
a. |
Chromatids are not involved in mitosis. |
|
b. |
Tetrads rarely form during mitosis. |
|
c. |
A cell undergoing mitosis does not have
homologous chromosomes. |
|
d. |
There is no prophase during mitosis. |
____††††††††† 190.††††††††††† Which of the following assort
independently?
|
a. |
chromosomes |
|
b. |
genes on the same chromosome |
|
c. |
multiple alleles |
|
d. |
codominant alleles |
____††††††††† 191.††††††††††† Linked genes
|
a. |
are never separated. |
|
b. |
assort independently. |
|
c. |
are on the same chromosome. |
|
d. |
are always recessive. |
____††††††††† 192.††††††††††† If the gene for seed color and the
gene for seed shape in pea plants were linked,
|
a. |
all of Mendelís F1 plants
would have produced wrinkled, green peas. |
|
b. |
Mendelís F2 plants would have
shown a different phenotype ratio for seed color and seed shape. |
|
c. |
Mendelís F1 plants would have
shown a different phenotype ratio for seed color and seed shape. |
|
d. |
all of Mendelís P plants would have
produced wrinkled, green peas. |
____††††††††† 193.††††††††††† Gene maps are based on
|
a. |
the frequencies of crossing-over between
genes. |
|
b. |
independent assortment. |
|
c. |
genetic diversity. |
|
d. |
the number of genes in a cell. |
____††††††††† 194.††††††††††† If two genes are on the same
chromosome and rarely assort independently,
|
a. |
crossing-over never occurs between the
genes. |
|
b. |
crossing-over always occurs between the
genes. |
|
c. |
the genes are probably located far apart
from each other. |
|
d. |
the genes are probably located close to
each other. |
____††††††††† 195.††††††††††† The farther apart two genes are
located on a chromosome, the
|
a. |
less likely they are to be inherited
together. |
|
b. |
more likely they are to be linked. |
|
c. |
less likely they are to assort independently. |
|
d. |
less likely they are to be separated by
a crossover during meiosis. |
____††††††††† 196.††††††††††† Averyís experiments showed that
bacteria are transformed by
|
a. |
RNA. |
|
b. |
DNA. |
|
c. |
proteins. |
|
d. |
carbohydrates. |
____††††††††† 197.††††††††††† What did Griffith observe when he
injected a mixture of heat-killed, disease-causing bacteria and live harmless
bacteria into mice?
|
a. |
The disease-causing bacteria changed
into harmless bacteria. |
|
b. |
The mice developed pneumonia. |
|
c. |
The harmless bacteria died. |
|
d. |
The mice were unaffected. |
____††††††††† 198.††††††††††† What would Hershey and Chase have
concluded if both radioactive 32P and 35S were found in
the bacteria in their experiment?
|
a. |
The virusís protein coat was not
injected into the bacteria. |
|
b. |
The virusís DNA was not injected into
the bacteria. |
|
c. |
Genes are made of protein. |
|
d. |
Both the virusís protein coat and its
DNA were injected into the bacteria. |
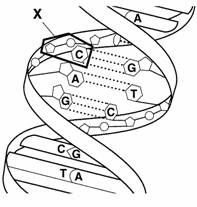
Figure 12-1
____††††††††† 199.††††††††††† Figure 12-1 shows the structure of
a(an)
|
a. |
DNA molecule. |
|
b. |
amino acid. |
|
c. |
RNA molecule. |
|
d. |
protein. |
____††††††††† 200.††††††††††† Which of the following is a
nucleotide found in DNA?
|
a. |
ribose + phosphate group + thymine |
|
b. |
ribose + phosphate group + uracil |
|
c. |
deoxyribose + phosphate group + uracil |
|
d. |
deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine |
____††††††††† 201.††††††††††† Because of base pairing in DNA, the
percentage of
|
a. |
adenine molecules in DNA is about equal
to the percentage of guanine molecules. |
|
b. |
pyrimidines in DNA is about equal to the
percentage of purines. |
|
c. |
purines in DNA is much greater than the
percentage of pyrimidines. |
|
d. |
cytosine molecules in DNA is much
greater than the percentage of guanine molecules. |
____††††††††† 202.††††††††††† DNA is copied during a process
called
|
a. |
replication. |
|
b. |
translation. |
|
c. |
transcription. |
|
d. |
transformation. |
____††††††††† 203.††††††††††† DNA replication results in two DNA
molecules,
|
a. |
each with two new strands. |
|
b. |
one with two new strands and the other
with two original strands. |
|
c. |
each with one new strand and one
original strand. |
|
d. |
each with two original strands. |
____††††††††† 204.††††††††††† During DNA replication, a DNA strand
that has the bases CTAGGT produces a strand with the bases
|
a. |
TCGAAC. |
|
b. |
GATCCA. |
|
c. |
AGCTTG. |
|
d. |
GAUCCA. |
____††††††††† 205.††††††††††† In eukaryotes, DNA
|
a. |
is located in the nucleus. |
|
b. |
floats freely in the cytoplasm. |
|
c. |
is located in the ribosomes. |
|
d. |
is circular. |
____††††††††† 206.††††††††††† During mitosis, the
|
a. |
DNA molecules unwind. |
|
b. |
histones and DNA molecules separate. |
|
c. |
DNA molecules become more tightly
coiled. |
|
d. |
nucleosomes become less tightly packed. |
____††††††††† 207.††††††††††† Which of the following include all
the others?
|
a. |
DNA molecules |
|
b. |
histones |
|
c. |
chromosomes |
|
d. |
nucleosomes |
____††††††††† 208.††††††††††† RNA contains the sugar
|
a. |
ribose. |
|
b. |
deoxyribose. |
|
c. |
glucose. |
|
d. |
lactose. |
____††††††††† 209.††††††††††† Unlike DNA, RNA contains
|
a. |
adenine. |
|
b. |
uracil. |
|
c. |
phosphate groups. |
|
d. |
thymine. |
____††††††††† 210.††††††††††† Which of the following are found in
both DNA and RNA?
|
a. |
ribose, phosphate groups, and adenine |
|
b. |
deoxyribose, phosphate groups, and
guanine |
|
c. |
phosphate groups, guanine, and cytosine |
|
d. |
phosphate groups, guanine, and thymine |
____††††††††† 211.††††††††††† How many main types of RNA are
there?
|
a. |
1 |
|
b. |
3 |
|
c. |
hundreds |
|
d. |
thousands |
____††††††††† 212.††††††††††† Which type(s) of RNA is(are)
involved in protein synthesis?
|
a. |
transfer RNA only |
|
b. |
messenger RNA only |
|
c. |
ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA only |
|
d. |
messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and
transfer RNA |
____††††††††† 213.††††††††††† Which of the following are copied
from DNA?
|
a. |
mRNA only |
|
b. |
mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA |
|
c. |
mRNA and tRNA only |
|
d. |
proteins |
____††††††††† 214.††††††††††† What is produced during
transcription?
|
a. |
RNA molecules |
|
b. |
DNA molecules |
|
c. |
RNA polymerase |
|
d. |
proteins |
____††††††††† 215.††††††††††† During transcription, an RNA
molecule is formed
|
a. |
that is complementary to both strands of
DNA. |
|
b. |
that is identical to part of a single
strand of DNA. |
|
c. |
that is double-stranded. |
|
d. |
inside the nucleus. |
____††††††††† 216.††††††††††† Which of the following statements is
true?
|
a. |
A promoter is part of an intron. |
|
b. |
A pre-mRNA molecule is longer than the
gene from which the molecule was transcribed. |
|
c. |
Introns have complementary sequences in
DNA. |
|
d. |
mRNA molecules made from the same gene
are always edited the same way. |
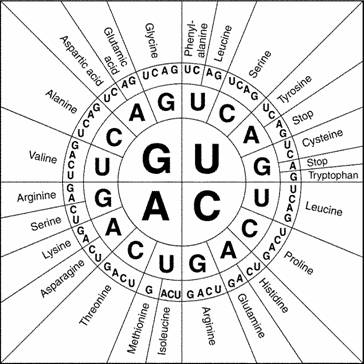
Figure 12-2
____††††††††† 217.††††††††††† What does Figure 12-2 show?
|
a. |
anticodons |
|
b. |
the order in which amino acids are
linked |
|
c. |
the code for splicing mRNA |
|
d. |
the genetic code |
____††††††††† 218.††††††††††† How many codons are needed to
specify three amino acids?
|
a. |
3 |
|
b. |
6 |
|
c. |
9 |
|
d. |
12 |
____††††††††† 219.††††††††††† Why is it possible for an amino acid
to be specified by more than one kind of codon?
|
a. |
Some codons have the same sequence of
nucleotides. |
|
b. |
There are 64 different kinds of codons
but only 20 amino acids. |
|
c. |
Some codons do not specify an amino
acid. |
|
d. |
The codon AUG codes for the amino acid
methionine and serves as the ďstartĒ codon for protein synthesis. |
____††††††††† 220.††††††††††† What happens during the process of
translation?
|
a. |
Messenger RNA is made from DNA. |
|
b. |
The cell uses information from messenger
RNA to produce proteins. |
|
c. |
Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA. |
|
d. |
Copies of DNA molecules are made. |
____††††††††† 221.††††††††††† Which of the following terms is
LEAST closely related to the others?
|
a. |
intron |
|
b. |
tRNA |
|
c. |
polypeptide |
|
d. |
anticodon |
____††††††††† 222.††††††††††† During translation, the type of
amino acid that is added to the growing polypeptide depends on the
|
a. |
codon on the mRNA only. |
|
b. |
anticodon on the mRNA only. |
|
c. |
anticodon on the tRNA to which the amino
acid is attached only. |
|
d. |
codon on the mRNA and the anticodon on
the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached. |
____††††††††† 223.††††††††††† Genes contain instructions for
assembling
|
a. |
purines. |
|
b. |
nucleosomes. |
|
c. |
proteins. |
|
d. |
pyrimidines. |
____††††††††† 224.††††††††††† Which type of RNA functions as a
blueprint of the genetic code?
|
a. |
rRNA |
|
b. |
tRNA |
|
c. |
mRNA |
|
d. |
RNA polymerase |
____††††††††† 225.††††††††††† Which of the following statements is
false?
|
a. |
Some genes code for enzymes. |
|
b. |
The instructions for making some
proteins are not specified by genes. |
|
c. |
An organismís inherited traits depend on
proteins. |
|
d. |
An organismís genes determine its
inherited traits. |
____††††††††† 226.††††††††††† A mutation that involves a single
nucleotide is called a(an)
|
a. |
chromosomal mutation. |
|
b. |
inversion. |
|
c. |
point mutation. |
|
d. |
translocation. |
____††††††††† 227.††††††††††† Which of the following is NOT a gene
mutation?
|
a. |
inversion |
|
b. |
insertion |
|
c. |
deletion |
|
d. |
substitution |
____††††††††† 228.††††††††††† Which of the following is NEVER a
frameshift mutation?
|
a. |
substitution |
|
b. |
insertion |
|
c. |
deletion |
|
d. |
point mutation |
____††††††††† 229.††††††††††† A promoter is a
|
a. |
binding site for DNA polymerase. |
|
b. |
binding site for RNA polymerase. |
|
c. |
start signal for transcription. |
|
d. |
stop signal for transcription. |
____††††††††† 230.††††††††††† Which of the following statements is
true?
|
a. |
A promoter determines whether a gene is
expressed. |
|
b. |
An expressed gene is turned off. |
|
c. |
Proteins that bind to regulatory sites
on DNA determine whether a gene is expressed. |
|
d. |
RNA polymerase regulates gene
expression. |
____††††††††† 231.††††††††††† If a specific kind of protein is not
continually used by a cell, the gene for that protein is
|
a. |
always transcribed. |
|
b. |
never expressed. |
|
c. |
turned on and off at different times. |
|
d. |
not regulated. |
____††††††††† 232.††††††††††† In E. coli, the lac
operon controls the
|
a. |
breakdown of lactose. |
|
b. |
production of lactose. |
|
c. |
breakdown of glucose. |
|
d. |
production of glucose. |
____††††††††† 233.††††††††††† A lac repressor turns off the
lac genes by
|
a. |
binding to the promoter. |
|
b. |
DNA polymerase. |
|
c. |
binding to the operator. |
|
d. |
binding to the lac genes. |
____††††††††† 234.††††††††††† When E. coli are grown on
glucose,
|
a. |
lactose molecules bind to the lac
repressor. |
|
b. |
the lac repressor binds to the
operator of the lac operon. |
|
c. |
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter of
the lac operon. |
|
d. |
the lac genes are transcribed. |
____††††††††† 235.††††††††††† Which of the following is NOT
generally part of a eukaryotic gene?
|
a. |
operon |
|
b. |
TATA box |
|
c. |
promoter sequences |
|
d. |
enhancer sequences |
____††††††††† 236.††††††††††† Gene regulation in eukaryotes
|
a. |
usually involves operons. |
|
b. |
is simpler than in prokaryotes. |
|
c. |
allows for cell specialization. |
|
d. |
includes the action of an operator
region. |
____††††††††† 237.††††††††††† Specialized cells regulate the
expression of genes because they
|
a. |
do not want the genes to become worn
out. |
|
b. |
cannot control translation. |
|
c. |
do not carry the complete genetic code
in their nuclei. |
|
d. |
do not need the proteins that are
specified by certain genes. |
____††††††††† 238.††††††††††† Hox genes determine an animalís
|
a. |
basic body plan. |
|
b. |
size. |
|
c. |
skin color. |
|
d. |
eye color. |
____††††††††† 239.††††††††††† Which of the following statements is
false?
|
a. |
Mutations do not occur in hox genes. |
|
b. |
Hox genes that are found in different
animals are very different from each other. |
|
c. |
Hox genes control the normal development
of an animal. |
|
d. |
Hox genes occur in clusters. |
____††††††††† 240.††††††††††† Hox genes
|
a. |
are regulated by operons. |
|
b. |
are found in bacteria. |
|
c. |
are not found in humans. |
|
d. |
determine the location of a dogís ears. |